What is 5G?
5G is not just an evolutionary upgrade from the previous generation of mobile communications, but a revolutionary technology designed to remove the limits of global connectivity for access, bandwidth, performance and latency. 5G has the potential to enable fundamentally new applications, industries and business models and dramatically improve quality of life around the world through unprecedented use cases requiring instant high data rate communications, low latency and massive connectivity for new applications, autonomous vehicles, smart cities, smart homes and the IoT.
5G connects Smart City and Smart Country
Smart Cities and Smart Country are connected ecosystems. Technologies related to connected vehicles, connected health, connected workplaces, public safety, utilities, governance, etc. are undergoing a digital transformation to meet the increasing demands of the future.
A robust communication infrastructure is crucial in this process for the necessary supply chains and communication links between the city and rural areas.
"Voice and video communication is only one application of 5G. [...] More important are the opportunities that low latency and high data rates bring to industry and IoT."
Prof. Dr. Thomas Magedanz | Fraunhofer FOKUS
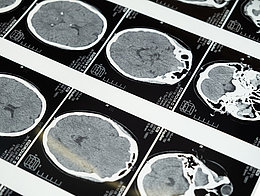
Healthcare worldwide is experiencing a paradigm shift with an increasing number of technologies (e.g. sensors and sensor data) and advances in telemedicine.
Connectivity is fundamental to the explosive growth in the number of machines and sensor-based applications (Massive-Machine Type Communication (mMTC)). 5G is mandatory for use cases such as Tactile Internet and remote robotic operations and the associated Critical Machine-Type Communication (cMTC) or Ultra Reliability and Low Latency Communications (URLLC).
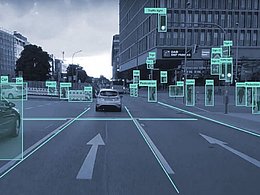
5G technologies will play a crucial role for the automotive industry. The ability for vehicles to exchange data in real time with other vehicles, pedestrians, and roadside infrastructure and application servers will enable the development of revolutionary services.
- Vehicle "platooning": vehicles dynamically forming a group, driving together and within a very short distance of each other
- "Advanced Driving": sharing of driving intentions, sensor data and collected video by on-board cameras with road infrastructure, other vehicles, pedestrians and network servers for safety and traffic efficiency applications and semi- or fully-automated driving
- Remote / cloud computing driving: Automated driving (in public spaces)